Cheminform Abstract Synthesis of Metal-organic Frameworks a Mini Review
Metallic Organic Frameworks
Aastha Goyal*
Section of Chemistry, Sri Guru Granth Sahib World Academy, Bharat
- *Corresponding Author:
- Aastha Goyal
Department of Chemistry
Sri Guru Granth Sahib Earth Academy, India
E-mail: [email protected]
Received Date: 06/09/2018; Accepted Date: 09/10/2018; Published Date: 11/01/2019
Visit for more related articles at Research & Reviews: Journal of Chemistry
Abstruse
In this review article, Metal organic frameworks were prepared by diverse routes and the prepared MOFs was characterized by various techniques similar Fourier transform-infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and Energy Dispersive X-ray (EDX) techniques. MOFs were prepared by combination of various inorganic metals and organic linkers. MOFs have potential for the treatment of various gaseous pollutants. Further, MOFs were used for making composites with the help of doping something similar ionic liquid, graphene oxide, CNTs etc. and these MOFs composite helpful in wide range of applications like gas storage, biomedical applications and catalysis and detection of heavy metal ions. MOFs take broad of advantageous properties (eastward.g., high surface area, loftier degree of porosity, specific adsorption affinities).
Keywords
Pharmacology, Calibrants, Relaxation, Deprotonation, Vacuum
Introduction
Porous materials embrace a wide range of uses in the industrial processes such as assimilation and catalysis and they are basically classified equally zeolites (inorganic hybrid), polymers (organic hybrid) and metal organic frameworks (inorganic-organic hybrid) [1]. Metallic organic frameworks (MOFs) are the microporous cloth (<2 nm), they are formed by linking metal (it tin exist ion and a metallic node) and organic linker by coordination bond [2]. The organic linkers are molecule or ion that can donate lonely pairs of electrons to the metallic ions, whereas the metallic ions have vacant orbital that can take these lone pairs of electrons from organic linkers to course a MOFs material. MOFs are subset of coordination networks which are again subset of coordination polymers. The topology of MOFs are depend on geometry of ligands and stability of MOFs is determined past metallic-linker combination [3].
They are called THE Hereafter because their composites such as ionic liquid - MOFs, graphene oxide-MOFs etc. are used to capture carbon dioxide which is a greenhouse effect and also store hydrogen gas which is a futurity fuel [4]. They accept other applications such equally dye deposition [5], detection of heavy metallic ions [6], sensors [7], drug delivery [viii], luminescence [9], magnetism [10], gas storage [eleven] and others has a broad range of applications equally they have slap-up porosity, specific adsorption affinities and specific surface area. MOFs are interesting over conventional materials similar zeolites, COFs and polymers, as diverse metals and organic linkers unite to grade a large number of materials with different crystal structures and chemical compositions. 1 can tune their backdrop according to applications that one requires and then due to their structural tunability and function ability, MOFs are excellent substitutes of conventional nanoporous material. The limitation of zeolites is that their pores are restricted. It is difficult to change these materials for specific use as they take rigid tetrahedral oxide skeletons whereas the pore sizes and chemical functionalities of MOFs can exist tuned by using different metal nodes to achieve a desired application [12]. They accept been studied for a variety of applications, such every bit gas storage and separation [13], biomedical applications [14], and catalysis [15]. In addition to MOFs, covalent organic frameworks (COFs) are those which accept like materials without metals are called COFs. They take lite elements such as H, B, C, Due north, and O, which form strong covalent bonds with each other [16]. COFs take lower densities than MOFs although they have similar characteristics as MOFs such as large surface areas, high pore volumes, and permanent porosities [17]. The synthesis of metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) involves the reaction of a metallic-containing precursor with an organic linker in an organic solvent at an elevated temperature, in what is termed a 'solvothermal' reaction. Many more examples have been reported of MOF synthesis in ionic liquids (ILs), rather than an organic solvent, in 'ionothermal' reactions [18].
Composites materials are those substances which contain ii or more materials that combine to produce a new substances with different physical properties from the original substances. When MOFs are doped with some other materials such as ionic liquid, graphene oxide, CNT and then composites are formed. As yet, MOF composites have been successfully incorporating with various metal or metallic oxides nanoparticles (NPs), carbon materials, polymers, polyoxometalates, ionic liquids, and then on (Figures 1 and 2) [xix].
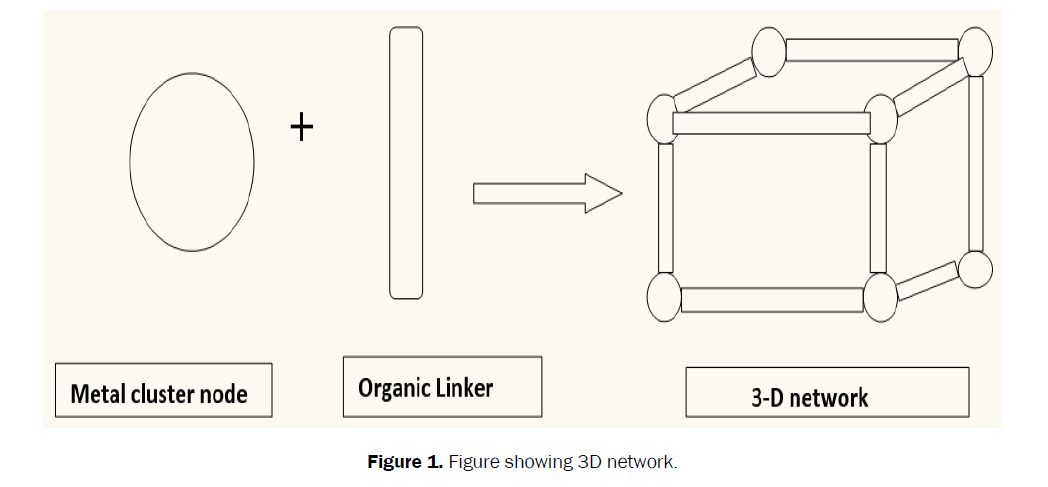
Figure i. Figure showing 3D network.
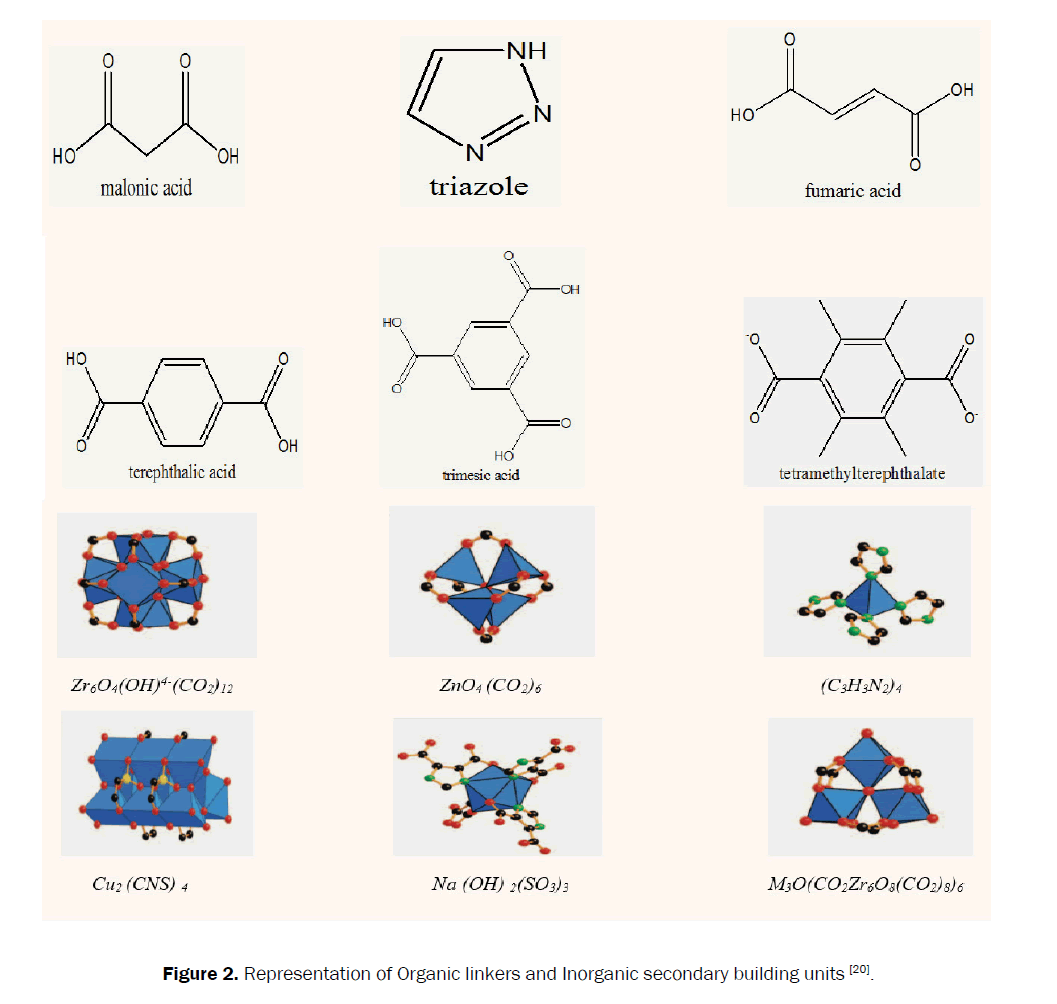
Figure 2. Representation of Organic linkers and Inorganic secondary building units [20].
Pattern of MOFs: First row transition metals such every bit Zn, Cu and Co are well known to be able to coordinate with organic groups under diverse methods like hydro and solvothermal conditions to form crystals.
Nomenclature
Manifestly because of the relatively brusque path of this family of materials, in that location is non a normalized nomenclature for MOFs (which is used for zeolites).
Some researchers gave the proper noun to metallic organic frameworks by consecutive number of synthesis/chronological sequence of findings, initials of organizations or institutions where they were initially prepared or by sequent of isorecticular synthesis.
Naming past sequent number of synthesis: In this method, the MOFs were named equally MOF-two, MOF-3, MOF-four, MOF-5, so on, where the number which fastened to MOFs designated every bit the chronological sequence of findings C40H56.
Naming past initials of organization or institution or place of finding: The second method to requite name to MOFs is done by forming a phrase or an acronym from the name of an organisation, identify or any institution where these crystalline MOFs was actually prepared eastward.k., HKUST-north36 (Hong Kong University of Science and Applied science), UiO-66 (University of Oslo).
Naming past consecutive of isorecticular synthesis: Isoreticular means same topology and the naming of MOFs were based on the topology of organic linkers that ways they share a common cubic topology which were made from the same type of organic linkers. e.g., IRMOF-ane and IRMOF-0 where IRMOF is Isoreticular metal organic frameworks.
An alternative to this illustrative name consists of using the "empirical formula" of the material, i.due east., expressing the metal(s), the ligand(s), and their stoichiometry in the repetitive unit of measurement, e.g., [Zn4(O)(bdc)3] (bdc)one,4-benzenedicarboxylate) [21].
History
The very first metal organic framework synthesized was MOF-two which has its formula Zn (BDC) (H2O) where BDC means 1, four-benzenedicarboxylate. Other such materials were synthesized which possess porosity were MOF-3 [Znthree(bdc)3 ] and MOF-4 [Zn(btc)NO3) where btc means 1,iii,5-benzentricarboxylate [22]. Werner has researched on coordination complexes. At that time many porous crystals were as well been identified [23]. Those identified porous crystals did not exhibit permanent porosity. Porous crystal having permanent porosity was invented in 1990s [24]. Yaghi was the scientist who has given the name to these porous crystals that was "Metal Organic Framework" [25].
The near flexible MOF named MOF-v having neutral framework of composition Zn4O(BDC) in which Zn4O groups are linked by terephthalate where BDC ways 1,4-dicarboxylate was synthesized in 1999 [26]. Its proper name was taken from a known zeolite ZSM-v [27].
Methods of Synthesis
The routine synthesis of metal organic frameworks were washed by solvothermal synthesis and hydrothermal methods. The other possibility for the synthesis of metal organic frameworks were done past, microwave-assisted synthesis, electrochemical synthesis, mechanochemical synthesis and sonochemical synthesis. Among all these methods, solvothermal and hydrothermal were popular techniques for the synthesis of MOFs because it is simple and easily controlled procedure. However, it has some disadvantages also such as information technology is time consuming and large particle size.
Solvothermal Synthesis
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) in which the reaction includes metallic-containing forerunner with an organic linker in an organic solvent at loftier temperature, in what is termed a 'solvothermal' reaction. In this method a mixture of both organic linkers and metal were heated at high temperature organic solvent. The thermal free energy (353 K-453 G) is applied to this process and this process could terminal between 48 to 96 hours. The organic solvents which were oftentimes used in solvothermal reactions were DMF (dimethylformamide), DEF (diethyl formamide), ethanol, methanol, acetone etc. For unlike kind of starting thing there will be a differing or varying solubility and to avoid this difficulty mixtures of solvents have been used. Solvothermal reactions tin be carried out in multifariousness of temperature ranges, depending on the required reaction. For the synthesis of inorganic compounds and MOFs (inorganic and organic hybrid), hydrothermal method has been successfully used [28]. For instance, Senkovska et al. synthesized 2 aluminium based metal-organic frameworks [Al(OH)(ndc)(DMF)1.5(H2O)one.v] and [Al(OH)(bpdc)(DMF)1.8(H2O)3.5] by solvothermal method using N,N-dimethylformamide as a solvent. In a typical synthesis, 2,6-naphthalene dicarboxylic acid or 4,4´-biphenyldicarboxylic acid respectively, was dissolved in DMF.Al (NO3)3.9H2O was added and the mixture was filled in a Teflon liner, placed in an autoclave, heated to 120°C for 24 h and cooled to room temperature. After the product was separated by centrifugation, the sediment was washed with DMF for three times and the product was dried on air [29]. Reinsch et al. synthesized the system Aliii +/H3BTB/DMF/additive was systematically investigated using high-throughput methods and the new, microporous MOF [Al (BTB)] (BTB=ane,3,5-benzenetrisbenzoate), named CAU-4 (CAU=Christian-Albrechts-University). The optimized synthesis of CAU-4 in the HT reactor organisation is as follows: Al (NO3)39H2O, benzoic acid and i,3,five-benzenetrisbenzoic acrid were dissolved in N,N-dimethylformamide. The reactor was heated for 24 h at 180°C. The reaction tin can be scaled up to the fourfold amount, using Pyrex drinking glass tubes, or to the tenfold amount, using larger steel autoclaves with Teflon inserts. The same molar ratios Aliii +: H3BTB: benzoic acid: DMF=7:fourteen:x:142 as well as the same temperature program were used. A yield of 47% (based on H3BTB) was obtained from the reaction in the 30 ml reactor [30]. Pradip et al. synthesized fluorinated MOFs by Solvothermal reactions of Cu(NOthree)2.3H2O with iv,40 -(hexafluoroisopropylidene) bis(benzoic acrid) (C17H10Fhalf dozenO4, H2hfbba) and last monodentate ligand 3-methyl pyridine (3-picoline/3-mepy) in the presence of N, Due north-dimethyl formamide (DMF) and N,Due north-diethyl formamide (DEF) solvents gave rise to two structurally dissimilar two dimensional (2D) fluorinated metal organic frameworks (FMOFs). The effect of the choice of solvent has been clearly reflected in the structures obtained. The F-MOFs reported in this paper are formulated as [Cu2(hfbba)2(three-mepy)2]. (DMF)2(three-mepy) (F-MOF-four), [Cu2(hfbba)2(3-mepy)2] (Cu-F-MOF-4B), and [Znii(hfbba)2(3-mepy)2]3(iii-mepy) (Zn-F-MOF-4B) which displays interesting 2nd structures with and without interdigitation depending on the solvent used.
Synthesis of [Cu2(hfbba)2(3-mepy)ii] (Cu-F-MOF-4B): 0.5 mL of 3-methyl pyridine stock solution and 1.5 mL of H2hfbba solution (0.20 M) in DEF were mixed in a v mL vial. 0.5 mL of Cu (NOthree)2 .3H2O solution (0.20 M) in DEF was added to this solution and it is heated at 85°C for 96 h and the products were washed with DEF (15 mL) three times. Nighttime blue colored crystals of Cu-F-MOF- 4B were collected by filtration and dried in air.
Synthesis of [Cu2(hfbba)2(3-mepy)2]three DMF)two(3-mepy) (F-MOF-4) 9b: 0.5 mL of 3-methyl-pyridine stock solution (0.twenty Yard) and 1.5 mL of Htwohfbba stock solution in DMF (0.20 M) were mixed in a 5 mL vial. 0.v mL of Cu(NOiii)2. 3H2O stock solution (0.xx K) was added to this solution and information technology is heated at 85°C for 96 and the products were washed with DMF (fifteen mL) three times. The blue colored crystals were collected by filtration and dried.
Synthesis of [Zn2(hfbba)2(3-mepy)2]3(3-mepy) (Zn-FMOF-4B): 0.five mL of 3-methyl pyridine stock solution and i.5 mL of H2hfbba solution (0.20 M) in DEF were mixed in a five mL vial. 0.v mL of Zn(NO3)2 6H2O solution (0.twenty M) in DEF was added to this solution and it is heated at 85°C for 96 h and the products were done with DEF (15 mL) iii times. Colorless crystals of Zn- F-MOF-4B were collected by filtration and dried in air [31].
Tian et al. synthesized nickel based MOF by using methanol equally solvent. Ni(NO3)3.6HtwoO and 2.four mmol of BTC were dissolved in seventy mL absolute methanol. The mixture was stirred for 1 h at room temperature, and and then transferred into a Tefon-lined stainless steel autoclave with a volume capacity of 100 mL and heated at 150°C for 24 h. Subsequently the oestrus treatment, the autoclave is immune to cool naturally to room temperature, and the products are collected by centrifugation at 10000 rpm for five min and washed with accented methanol several cycles, and then dried at 60°C in vacuum 12 h. Glover synthesized various MOF-74 edifice units using cobalt, magnesium, zinc, nickel metallic centres [32].
Cobalt MOF-74 (Co-MOF-74): In a 400 mL jar, with sonication, 0.v thou of two,5 dihydroxyterephthalic acid (DHTA) and 1.5 thousand of Co(NO3)2 .6HiiO were dissolved in dimethylformamide, ethanol, and water. The jar was capped tightly and placed in a 100°C oven for ii.75 days. After cooling, mother liquor was decanted and the products were washed with methanol and immersed in methanol. The products were and so evacuated to dryness and heated under vacuum to 250°C. Subsequently 24 h, the sample was cooled to room temperature and stored [33].
Petit and Bandosz synthesized MOF- 5: MOF-5 was prepared by mixing zinc nitrate hexahydrate and 1,4-benzenedicarboxylate in Due north,N-dimethylformamide (DMF, 140 mL) until complete dissolution of the solids. So, the mixture was transferred into a round-bottom flask connected to a condenser and heated at 115-120°C for 24 h. After cooling, the supernatant was removed and crystals deposited on the bottom of the flask were nerveless, done with DMF, and immersed in fresh chloroform overnight. The chloroform was changed twice during ii days. Finally, crystals were collected, placed inside a closed filtering flask connected to an aspirator, used to create vacuum inside the flask, and heated at 130-135°C for 6 h. The resulting crystals were then kept in a desiccator [34].
Mueller et al. synthesized MOF-2. MOF-2 was prepared by mixing 24.9 yard of terephthalic acrid (BDC) and 52.2 thousand of zinc nitrate tetrahydrate (Merck) were dissolved in 43.6 chiliad of Due north-methyl-two- pyrrolidone, 8.6 g of chlorobenzene and 24.9 g of dimethylformamide and heated upwards to 70 μC for a total of 3 h. Afterwards hour, 30 yard triethylamine was added. Later filteration, white precipitates was formed which was stale in air. The molar yield based on zinc amounted to 87% [35].
Microwave Assisted Synthesis
MOFs were synthesized very quickly by using microwave-assisted synthesis method. As solvothermal method, this method also brand nanosized MOFs crystals very chop-chop. The advantages of this method includes rapid crystallization, stage selectivity, small particle size distribution, and facile morphology command. The crystals were obtained by heating a solution of metal table salt, organic linker, organic solvent which kept in microwave at 303 K-373 One thousand. The kind of crystals which were made past microwave-assisted method were similar as produced by solvothermal method. The get-go reported MOFs by microwave synthesis was Cr-MIL-100 [36].
Jianwei Ren et al. synthesized Zr-based MOFs by microwave-assisted method: The microwave-assisted synthesis of Zr-MOFs was conducted in a microwave reaction system (Anton Paar Synthos 3000). Information technology was prepared by 0.75 thou terephthalic acid and ane.05 one thousand zirconium tetrachloride were dissolved in 40 ml DMF ultrasonically and add 17 ml formic acid to that solution and that solution was divided into four portions. Iv microwave vessels were programmed for reaction at 120ºC for v min under static conditions. After reaction, the sample was treated in the aforementioned style every bit the Zr-MOF-Oven sample [37].
Choi et al. synthesized MOF-5 past MW:MOF-v was synthesized in Northward,N'-diethylformamide (DEF) using microwave irradiation. Equimolar amount of HtwoBDC (1.57 mg, 0.60 × 10-ii mmol) and zinc nitrate tetrahydrate (1.50 mg, 0.60 × ten-two mmol) in a DEF (0.6 mL) were place in a 10 mL tube and the tube was sealed and placed in a microwave oven (Discover, CEM, maximum ability of 300 W). The resulting mixture was heated at 95°C, held for 9 min and then cooled to room temperature. The colorless crystalline materials (2.10 mg, 27% yield) were obtained by centrifuging, washing with N,North'-dimethylformamide (DMF, iii × 5 mL) and drying briefly in the air [38].
In this method of synthesis metallic ions were used instead of metallic salts and these metallic ions were supplied constantly through aniodic dissolution which act as a metal source and these metallic ions were react with the mixture that contain both organic linkers and electrolytes. The electrochemical synthesis of MOFs was first reported in 2005 by researchers at BASF for HKUST-1. In this MOFs were synthesized past electrochemical route for e.g. bulk copper plates were arranged as the anodes in an electrochemical cell with the carboxylate linker, viz. one,3,five-benzenetricarboxylic acid, dissolved in methanol as solvent and a copper cathode a light-green blue precipitate was formed. The pure Cu-MOF was obtained and after activation at 250°C a night blue coloured solid of octahedral crystals is formed. For certain applications information technology is necessary to synthesized large crystals nether moderate atmospheric condition by adjusting some parameters like pH/solvent at room temperature [39].
Mueller et al. synthesized Cu-MOF using an electrochemical road: Bulk copper plates, thickness 5 mm, are arranged as the anodes in an electrochemical cell with the carboxylate linker, viz. one,3,five-benzenetricarboxylic acid, dissolved in methanol equally solvent and a copper cathode. Details are to exist institute in. x During a period of 150 min at a voltage of 12–nineteen V and a currency of 1.3 A, a green blue precipitate was formed. Afterward separation past filtration and drying at 120 uC overnight pure Cu-MOF was obtained which was dark blue coloured solid of octahedral crystals from 0.5 to 5 mm size [twoscore].
Mechanochemical synthesis
Mechanochemical is basically combination of mechanical strength and chemical reactions, then it is clear from the name mechanochemical synthesis that information technology is a solvent gratis procedure which can occur at room temperature where MOFs were constructed via a process of performing diverse chemical reactions past applying mechanical force. To become a desired MOFs, a mixture of both metal salts and linkers were ground together in a brawl mill. Mechanochemical synthesis of a Cu-isonicotinic acid MOF was starting time reported in 2006 by Pichon et al. Recently for the rapid synthesis of MOFs, LAG (Liquid Assisted Grinding) is used. In Liquid Assisted grinding procedure a pocket-size corporeality of solvent was added into a reaction mixture for e.yard., different solvent was added to a mixture of fumaric acid and ZnO, and they form 1D, 2nd, and 3D coordination polymers. The liquid can also human activity every bit construction directing agent. For the synthesis of pillared MOFs there was expansion of LAG (liquid assisted grinding) to ILAG (ion- and liquid assisted grinding). The advantage of this method is over other method such as sonochemical and microwave assisted synthesis is that mechanochemical synthesis is solvent free while sonochemical and microwave methods were still depend on organic solvent. Withal, mechanochemical synthesis is limited to specific MOF types simply and large amount of production is hard to obtain and one drawback about this method is that it was limited for particular types of MOFs and immense amount of issue was difficult to acquire [41].
Klimakow et al. carried out mechanochemical synthesis in a conventional ball manufactory via the liquid-assisted grinding of fine powders of copper acetate monohydrate and 1,iii,5-benzenetricarbocylic acid (H3BTC) and copper acetate monohydrate and 4, twoscore, 400- benzenetribenzoic acrid (H3BTB), respectively, in a molar ratio of 3:ii for 25 min. The color of the pulverisation inverse during the reaction from deep green to bluish, accompanied by the stiff olfactory property of the byproduct, acerb acid [42].
Sonochemical Synthesis
Sonochemistry is a procedure in which molecules undergo chemical change due to the application of intensive ultrasound radiations between xx kHz and10 MHz. As compared to conventional solvothermal methods this method create homogeneous and accelerated nucleation which tin also requite a minimal crystallization fourth dimension and appreciably using sonochemical irradiation in 1- methyl-2-pyrrolidinone (NMP) can produce 5–25 mm crystals in 30 min, which is similar to MOF-5 synthesized past solvothermal or microwave methods [43].
Tahmasian et al. synthesized {[Mg(HIDC)(H2O)two].ane.5H2O}n nanostructure by using Sonochemical Method. To prepare nano-sized {[Mg(HIDC)(H2O)2].1.5H2O}n, 20 mL of an aqueous solution of the ligand H3IDC (0.05 M) and potassium hydroxide (0.1 Thousand). Into the solution of H3IDC and potassium hydroxide, add 20 mL of an aqueous solution of magnesium nitrate (0.05 M) was added dropwise. The obtained precipitates were filtered off, washed with water and ethanol, and air-stale [44].
Other Methods
Ionothermal Synthesis
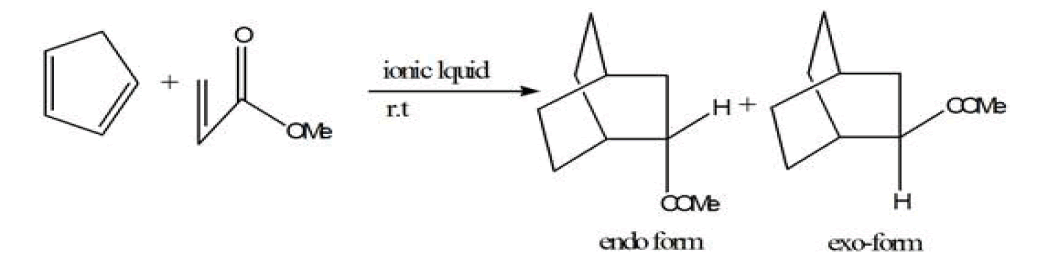
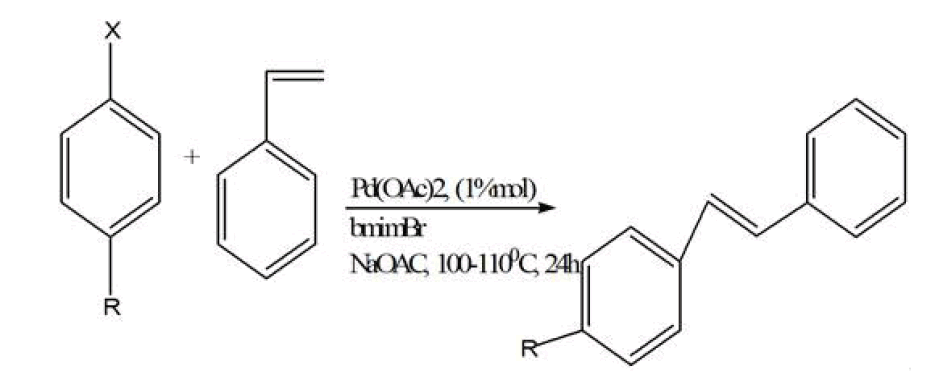
Metal organic frameworks were synthesized in ionic liquid rather than organic solvent is known as ionothermal reactions. Ionic liquids are defined equally materials that are composed entirely of ions and that take a melting indicate below 373 K [45]. Ionic liquids take salient features like low vapor force per unit area at room temperature,[46] nonvolatile,[47] nonflammable,[48] recyclable, high thermal stability, varying polarity, loftier electrical conductivity. Ionic liquid are called 'liquids' because the cations are asymmetrically substituted with different bulky groups which weaken the ionic interactions and they too prevents packing of the anions/cations into a crystal lattice. The high concentration of both organic cations (east.one thousand., imidazolium, pyrrolidinium, pyridinium,) and inorganic or organic anions (eastward.chiliad., tetrafluoroborate, hexafluorophosphate, and bromide) in an ionic liquid allows for the formation of new MOF structures by incorporating both anions and cations into the open cavities of MOFs. In this method of synthesis both cations and -anions were trapped or fused into MOFs. In well-nigh of the cases cationic part of ionic liquid was included in the pores of MOF, whereas anionic charge of MOFs human activity as a counter ion and MOF construction forms. Ionic liquid human action as solvent and template or construction directing agent. It is synthesized in ionic liquid at room temperature by the starting precursors of MOFs with the aid of modulator which initiate the reaction then this mixture is sealed within Teflon-lined stainless-steel autoclave then it is placed into the furnace by providing detail temperature for some days. Somewhen, it is cool down at standard temperature and crystals are collected. Also the formation of MOFs by Ionic liquids, ionic liquids also accept not bad importance in the synthesis of organic reactions similar Diels-Alder reaction, Heck reaction, etc.
Diels-Alder reaction
Heck reaction
References
- Jian-Rong L, et al. Postsynthetic Methods for the Functionalization of Metal–Organic Frameworks. Chem Rev 2012;112:869-932.
- Yu-Ri L. Synthesis of metallic-organic frameworks: A mini review. Korean J Chem Eng 2013;30:1667-1680.
- Fatma PK, et al. Ionic Liquid/Metal–Organic Framework Composites: From Synthesis to Applications. Chem Sus Chem 2017;10:2842-2863.
- Cheetam AK, et al. Structural diversity and chemical trends in hybrid inorganic–organic framework materials. Chem Commun 2006;5:4780-4795.
- Ling Q, et al. Photodegradation of Some Organic Dyes over Two Metallic–Organic Frameworks with Especially High Efficiency for Safranine T. Cryst Growth Des 2017.
- Lauren Eastward, et al. Metal-Organic Framework Materials every bit Chemical Sensors. Hupp Chem Rev 2012;112:1105-1125.
- Horcajada P. Porous metallic-organic-framework nanoscale carriers as a potential platform for drug commitment and imaging. Nat Mater 2010;9:172-178.
- Mohamedally Thou. Magnetic metal–organic frameworks. Chem Soc Rev 2009;38:1353-1379.
- Xin-Hui Z, et al. A flexible Eu(3)-based metal–organic framework: turn-off luminescent sensor for the detection of Fe(III) and picric acid. Dalton Trans 2013;42:12403-12409.
- Fatma PK, et al. Ionic Liquid/Metal–Organic Framework Composites: From Synthesis to Applications. Chem Sus Chem 2017;10:2842-2863.
- Adatoz E, et al. Graphene-based Membranes for Mass Transport. Applications Technol 2015;152:207-237.
- Qiu S, et al. Metal-organic framework membranes: from synthesis to separation awarding. Chem Soc Rev 2014;43:6116-6140.
- Rocca DJ, et al. Nanoscale Metal–Organic Frameworks for Biomedical Imaging and Drug Delivery. Chem Res 2011;44:957–968.
- Li Z, et al. Metal–Organic Frameworks for Heterogeneous Bones Catalysis. Chem Rev 2017;117:8129-8176.
- Keskin South and Kızılel S. Biomedical Applications of Metallic Organic Frameworks. Ind Eng Chem Res 2011;fifty:1799-1812.
- Liu Y, et al. Molecular Simulation of Carbon Dioxide/Methyl hydride/Hydrogen Mixture Adsorption in Metal−Organic Frameworks. Ind Eng Chem Res 2010;49:2902-2906.
- Yhomas VP. et al. Structure-directing effects of ionic liquids in the ionothermal synthesis of metal–organic frameworks. I U Cr J 2017;4:380-392.
- Kazuyuki F, et al. Low temperature ionic conductor: ionic liquid incorporated within a metal–organic framework. Chem Int Edn 2014;53:1-5.
- Hiroyasu F, et al. The Chemical science and Applications of Metallic-Organic Frame works. Science 2013;341:1230444.
- Ebelegi NA, et al. Metal-organic Frameworks as Novel Adsorbents: A Preview. American Journal of Environmental Protection 2017;five:61-67.
- Li H, et al. Room temperature synthesis of metal-organic frameworks: MOF-5, MOF-74, MOF-177, MOF-199, and IRMOF-0. Nature 1999;402:276-279.
- Furukawa H, et al. The chemistry and applications of metallic-organic frameworks. Science 341;123044.
- Kitagawa S, et al. Functional Porous Coordination Polymers. Angewandte Chemie International edn 2013;43:2334-2375.
- Thomas P, et al. Metal carbonate complexes formed through the capture of ambience O2 and CO2 by elemental metals in 1-methylimidazole: molecular Cu(CO3)(MeIm)3 and polymeric M(CO3)(MeIm)2·2H2O (M = Co, Zn). J Chem 2017;4:380-392.
- Schoedel A and Yaghi OM. Porosity in Metal-Organic Compounds: How Izatt-Christensen Laurels Winners Shaped the Field. Microcyclic and Supramolecular Chemistry 2016; pp: 201-219.
- Eddaoudi Thou, et al. Systematic design of pore size and functionality in isoreticular MOFs and their application in marsh gas storage. Science 2002;295:469-472.
- Thomas P, et al. Predictive tools in VVECMO patients: handicap or benefit for clinical practice. J Thorac Dis 2017;4:380-392.
- Irena Due south, et al. New highly porous aluminium based metal-organic frameworks: Al(OH)(ndc) (ndc=2,vi-naphthalene dicarboxylate) and Al(OH)(bpdc) (bpdc=4,4′-biphenyl dicarboxylate). Microporous and Mesoporous Materials 2009;122:93-98.
- Helge R, et al. A new aluminium-based microporous metal–organic framework: Al(BTB) (BTB=one,3,5-benzenetrisbenzoate). Microporous and Mesoporous Materials 2012;157:l-55.
- Pradip P, et al. Structural Multifariousness in Partially Fluorinated Metallic Organic Frameworks (F-MOFs) Composed of Divalent Transition Metals, 1,x-Phenanthroline, and Fluorinated Carboxylic Acid. Cryst Growth Des 2011;11:1215–1222.
- Tian T, et al. Metallic–organic framework-derived nickel phosphides as efficient electrocatalysts toward sustainable hydrogen generation from water splitting. RSC Adv 2015;5:10290.
- Grant 1000, et al. MOF-74 edifice unit has a direct affect on toxic gas adsorption. Chemical Technology 2011;66:170.
- Camille P and Teresa J. MOF–Graphite Oxide Composites: Combining the Uniqueness of Graphene Layers and Metal–Organic Frameworks. Bandosz Adv Mater 2009;21:4753-4757.
- Mueller U, et al. J Mater Chem 2006;16:626–636.
- Hindelang K, et al. Metal-organic Frameworks as Novel Adsorbents: A Preview. Chem Commun 2012;48:2888-2890.
- Jianwei R, et al. Microwave-assisted modulated synthesis of zirconium-based metal–organic framework (Zr-MOF) for hydrogen storage applications. Int J Mater Res 2014;105:one-iv.
- Jae YC, et al. Microwave Synthesis of a Porous Metal-Organic Framework Zinc Terephthalate MOF-5. Bull Korean Chem Soc 2006;27:1523.
- Heather F, et al. Zinc Terephthalate MOF-5. Korean Chem Soc 2006;27:10.
- Martinea A, et al. Electrochemical Synthesis of Some Archetypical Zn2+, Cu2+, and Al3+ Metallic Organic Frameworks. Cryst Growth Des 2012;seven:3489-3498.
- Mueller UM. Metal-organic frameworks-prospective industrial applications. J Mater Chem 2006;sixteen:626-636.
- Jean-Louis D and Frisic T. Metal-organic Frameworks as Novel Adsorbents: A Preview. ACS Cent 2016.
- Maria Thou, et al. Mechanochemical Synthesis of Metal-Organic Frameworks: A Fast and Facile Approach toward Quantitative Yields and High Specific Surface Areas. Chem Mater 2010;22:5216-5221.
- Carson CG, et al. Metal-organic Frameworks equally Novel Adsorbents: A Preview. Sonochemical Cryst Growth Des 2011;ten:4505-4510.
- Arineh T, et al. Sonochemical Syntheses of a One-Dimensional Mg(Two) Metal-Organic Framework: A New Precursor for Preparation of MgO One-Dimensional Nanostructure. Journal of Nanomaterials 2013;7:1.
- Gutowski KE, et al. Predictive thermodynamics for ionic solids and liquids. J Phys Chem 2005;109:23196-23208.
- Keith EJ. The Electrochemical Society Interface 2007.
- Vaid TP, et al. Structure-directing effects of ionic liquids in the ionothermal synthesis of metal–organic frameworks. International Union of Crystallography 2017;iv:380-392.
- Fatma PK, et al. Improving Gas Separation Operation of ZIF-viii by [BMIM][BF4] Incorporation: Interactions and Their Consequences on Performance. Chem Sus Chem 2017;10:2842-2863.
Source: https://www.rroij.com/open-access/metal-organic-frameworks.php?aid=87591
0 Response to "Cheminform Abstract Synthesis of Metal-organic Frameworks a Mini Review"
Post a Comment